Propane Microgrids for Disaster Preparedness
As the United States grapples with an aging and vulnerable electric grid, the frequency of unplanned outages has surged. Federal databases from the Department of Energy (DOE) and the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) reveal a steady increase in outages lasting more than an hour over the past decade, making the U.S. the leader in blackouts among developed nations. This escalating problem calls for innovative solutions, and one promising approach is the integration of propane microgrids.
The Microgrid Revolution
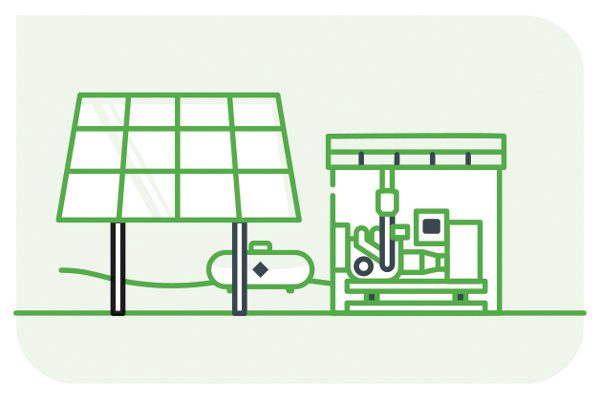
Unplanned outages not only disrupt daily life but pose serious threats to vital systems in commercial buildings. Smoke and fire detection, elevators, refrigeration units, and health and safety equipment are just a few examples of the critical systems impacted. Enter microgrids – localized energy grids capable of disconnecting from the traditional grid and operating autonomously. These microgrids incorporate distributed energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and generators, ensuring power during outages.
Propane’s Prowess in Microgrids
Propane stands out as a robust solution for microgrids, offering economic and environmental benefits crucial for disaster preparedness. Easily transportable and storable on-site for indefinite periods, propane emerges as the optimal low-carbon energy source for microgrids, aligning with the quest for a more reliable, secure, and clean energy system.
The Propane Education and Research Council’s (PERC) analysis, “The Opportunity for Propane in Microgrids,” underscores the competitive edge of propane generators in hybrid microgrids for commercial applications. Propane not only rivals diesel in cost but boasts lower emissions, comparable levelized costs of electricity, and enhanced resiliency.
Propane’s Environmental Impact
Severe weather events and natural disasters have catalyzed a surge in generator sales, historically dominated by diesel. However, PERC data supports propane as a cleaner alternative. In their study, “Power Generation: The Emissions Shifting Problem,” PERC explores how propane microgrid applications significantly improve local air quality by mitigating health-hazardous nitrogen oxides and particulate matter.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), propane outshines diesel, emitting 16 percent less CO2 per unit of energy. Moreover, the study introduces the concept of renewable propane, produced from sustainable materials, further reducing emissions and providing a cleaner alternative for microgrid applications.
Propane’s Role in Resilient Microgrids
Microgrids enhance the resiliency of local electricity distribution systems, especially crucial in areas prone to disasters. A notable case is the collaboration between solar energy company BoxPower and generator manufacturer Generac in Mariposa County, California. Here, a microgrid solution—featuring solar PV, battery backup, and a propane generator—provides a reliable power alternative, mitigating the risk of wildfires and forest fires.
In the event of larger-scale emergencies, microgrids can “island” their service area, detaching from the main electrical grid to continue providing electricity until restoration. A prime example is found in the U.S. Virgin Islands, where propane combines with solar power to reduce emissions by up to 20 percent, meeting clean air standards and cutting future fuel surcharges.
Propane microgrids emerge as a beacon of resilience in the face of escalating outages and disasters. Propane’s versatility, low environmental impact, and role in innovative microgrid solutions position it as a key player in safeguarding communities, businesses, and critical infrastructure. Propane microgrids not only offer a lifeline during outages but pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.










